环境
flannel版本: v0.12.0
外部网卡获取
外部网卡结构体
type ExternalInterface struct {
// 网卡属性
Iface *net.Interface
// 对应网卡的内部IP
IfaceAddr net.IP
// 对应网卡的外部IP(类似浮动IP)
ExtAddr net.IP
}
主处理函数逻辑
// Work out which interface to use
var extIface *backend.ExternalInterface
var err error
// Check the default interface only if no interfaces are specified
// 如果flannel启动程序没有指定网卡的话,即没有传入--iface或--iface-regex
if len(opts.iface) == 0 && len(opts.ifaceRegex) == 0 {
// --public-ip: 给其它节点内部访问用
// 根据传入的--public-ip,匹配对应的网卡,外部IP=publicIP;
// 如果没有--public-ip,则选择默认网关所在的网卡;外部IP=网卡IP
extIface, err = LookupExtIface(opts.publicIP, "")
if err != nil {
log.Error("Failed to find any valid interface to use: ", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
} else {
// Check explicitly specified interfaces
// 传入--iface参数,iface是一个string的slice
for _, iface := range opts.iface {
// 根据网卡名称匹配网卡, IP处理逻辑跟上面的一样
extIface, err = LookupExtIface(iface, "")
if err != nil {
log.Infof("Could not find valid interface matching %s: %s", iface, err)
}
// 找到就退出循环
if extIface != nil {
break
}
}
// Check interfaces that match any specified regexes
if extIface == nil {
// ifaceRegex也是一个string的slice, 可以定义正则表达式来匹配
for _, ifaceRegex := range opts.ifaceRegex {
// 正则表达式匹配两种场景,1. 先匹配IP 2. 如果没找到,再匹配网卡名
extIface, err = LookupExtIface("", ifaceRegex)
if err != nil {
log.Infof("Could not find valid interface matching %s: %s", ifaceRegex, err)
}
// 找到就退出循环
if extIface != nil {
break
}
}
}
// 都没匹配到的话,退出程序
if extIface == nil {
// Exit if any of the specified interfaces do not match
log.Error("Failed to find interface to use that matches the interfaces and/or regexes provided")
os.Exit(1)
}
}
节点本地子网分配
网络配置结构体
type Config struct {
Network ip.IP4Net
SubnetMin ip.IP4
SubnetMax ip.IP4
SubnetLen uint
BackendType string `json:"-"`
Backend json.RawMessage `json:",omitempty"`
}
func ParseConfig(s string) (*Config, error) {
cfg := new(Config)
// 这里注意Config中的Network、SubnetMin、SubnetMax自定义了MarshalJSON和UnmarshalJSON函数
// 例如:"Network": "172.28.0.0/16", PrefixLen就是16
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(s), cfg)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 对SubnetLen和PrefixLen值的判断
if cfg.SubnetLen > 0 {
// SubnetLen needs to allow for a tunnel and bridge device on each host.
if cfg.SubnetLen > 30 {
return nil, errors.New("SubnetLen must be less than /31")
}
// SubnetLen needs to fit _more_ than twice into the Network.
// the first subnet isn't used, so splitting into two one only provide one usable host.
if cfg.SubnetLen < cfg.Network.PrefixLen+2 {
return nil, errors.New("Network must be able to accommodate at least four subnets")
}
} else {
// If the network is smaller than a /28 then the network isn't big enough for flannel so return an error.
// Default to giving each host at least a /24 (as long as the network is big enough to support at least four hosts)
// Otherwise, if the network is too small to give each host a /24 just split the network into four.
if cfg.Network.PrefixLen > 28 {
// Each subnet needs at least four addresses (/30) and the network needs to accommodate at least four
// since the first subnet isn't used, so splitting into two would only provide one usable host.
// So the min useful PrefixLen is /28
return nil, errors.New("Network is too small. Minimum useful network prefix is /28")
} else if cfg.Network.PrefixLen <= 22 {
// Network is big enough to give each host a /24
// prefix为22,统一子网长度为24
cfg.SubnetLen = 24
} else {
// Use +2 to provide four hosts per subnet.
// 22 < prefix <= 28时, 统一子网长度=prefix+2
cfg.SubnetLen = cfg.Network.PrefixLen + 2
}
}
// subnetSize = ip.IP4(1 << (32 - 24)) = 256
subnetSize := ip.IP4(1 << (32 - cfg.SubnetLen))
// 如果没有定义SubnetMin
if cfg.SubnetMin == ip.IP4(0) {
// skip over the first subnet otherwise it causes problems. e.g.
// if Network is 10.100.0.0/16, having an interface with 10.0.0.0
// conflicts with the broadcast address.
// cfg.Network.IP = ParseIP4("172.28.0.0") = 2887516160
cfg.SubnetMin = cfg.Network.IP + subnetSize
} else if !cfg.Network.Contains(cfg.SubnetMin) {
return nil, errors.New("SubnetMin is not in the range of the Network")
}
// 如果没有定义SubnetMax
if cfg.SubnetMax == ip.IP4(0) {
// cfg.Network.Next().IP = 2887516160 + (1<<16)
cfg.SubnetMax = cfg.Network.Next().IP - subnetSize
} else if !cfg.Network.Contains(cfg.SubnetMax) {
return nil, errors.New("SubnetMax is not in the range of the Network")
}
// The SubnetMin and SubnetMax need to be aligned to a SubnetLen boundary
// 255.255.255.0
mask := ip.IP4(0xFFFFFFFF << (32 - cfg.SubnetLen))
if cfg.SubnetMin != cfg.SubnetMin&mask {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("SubnetMin is not on a SubnetLen boundary: %v", cfg.SubnetMin)
}
if cfg.SubnetMax != cfg.SubnetMax&mask {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("SubnetMax is not on a SubnetLen boundary: %v", cfg.SubnetMax)
}
bt, err := parseBackendType(cfg.Backend)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
cfg.BackendType = bt
return cfg, nil
}
等初始化完subnet管理器、backend管理器后,就把subnet配置信息写入本地文件
if err := WriteSubnetFile(opts.subnetFile, config.Network, opts.ipMasq, bn); err != nil {
// Continue, even though it failed.
log.Warningf("Failed to write subnet file: %s", err)
} else {
log.Infof("Wrote subnet file to %s", opts.subnetFile)
}
子网管理器
子网管理器有两种:一种是基于k8s实现的子网管理器,另一种是基于etcd实现的子网管理器
管理器的接口定义
type Manager interface {
GetNetworkConfig(ctx context.Context) (*Config, error)
AcquireLease(ctx context.Context, attrs *LeaseAttrs) (*Lease, error)
RenewLease(ctx context.Context, lease *Lease) error
WatchLease(ctx context.Context, sn ip.IP4Net, cursor interface{}) (LeaseWatchResult, error)
WatchLeases(ctx context.Context, cursor interface{}) (LeaseWatchResult, error)
Name() string
}
k8s子网管理器
如果启用了--kube-subnet-mgr, 集群中的每个节点子网分配取决于kube-controller-manager的--node-cidr-mask-size-ipv4=24和--node-cidr-mask-size-ipv6=64,
默认–node-cidr-mask-size-ipv4的值是24,–node-cidr-mask-size-ipv6的值是64,这两个值会影响到node.spec.podCidrs;没有使用到节点本地子网分配逻辑
type kubeSubnetManager struct {
// 节点的annotaions记录子网分配信息
annotations annotations
// k8s clientSet
client clientset.Interface
// 节点名称
nodeName string
// nodeLister
nodeStore listers.NodeLister
// Controller实例
nodeController cache.Controller
// 子网配置
subnetConf *subnet.Config
// Event channel,用于Backend类型与Controller之间通信
events chan subnet.Event
}
实际上这是一个监听Node事件的控制器, 估计是比较早期实现的,跟最新的sample-controller写法有异
func newKubeSubnetManager(c clientset.Interface, sc *subnet.Config, nodeName, prefix string) (*kubeSubnetManager, error) {
var err error
var ksm kubeSubnetManager
// 初始化annotations对象,用于标注在K8s Node对象上
ksm.annotations, err = newAnnotations(prefix)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
ksm.client = c
ksm.nodeName = nodeName
ksm.subnetConf = sc
ksm.events = make(chan subnet.Event, 5000)
// 初始化Indexer, Infromer对象
indexer, controller := cache.NewIndexerInformer(
// 定义List/Watch函数
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return ksm.client.CoreV1().Nodes().List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return ksm.client.CoreV1().Nodes().Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.Node{},
resyncPeriod,
// Add/Delete/Update Node事件对应的回调处理函数
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
ksm.handleAddLeaseEvent(subnet.EventAdded, obj)
},
UpdateFunc: ksm.handleUpdateLeaseEvent,
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
node, isNode := obj.(*v1.Node)
// We can get DeletedFinalStateUnknown instead of *api.Node here and we need to handle that correctly.
if !isNode {
deletedState, ok := obj.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
glog.Infof("Error received unexpected object: %v", obj)
return
}
node, ok = deletedState.Obj.(*v1.Node)
if !ok {
glog.Infof("Error deletedFinalStateUnknown contained non-Node object: %v", deletedState.Obj)
return
}
obj = node
}
ksm.handleAddLeaseEvent(subnet.EventRemoved, obj)
},
},
cache.Indexers{cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc},
)
ksm.nodeController = controller
ksm.nodeStore = listers.NewNodeLister(indexer)
return &ksm, nil
}
Add/Update Node事件的处理函数逻辑差不多
func (ksm *kubeSubnetManager) handleAddLeaseEvent(et subnet.EventType, obj interface{}) {
n := obj.(*v1.Node)
// 校验节点annotations中flannel.alpha.coreos.com/kube-subnet-manager
if s, ok := n.Annotations[ksm.annotations.SubnetKubeManaged]; !ok || s != "true" {
return
}
// 解析节点Node annotaions中的子网信息赋值给Lease对象
l, err := ksm.nodeToLease(*n)
if err != nil {
glog.Infof("Error turning node %q to lease: %v", n.ObjectMeta.Name, err)
return
}
// 塞到events channel中
ksm.events <- subnet.Event{et, l}
}
func (ksm *kubeSubnetManager) handleUpdateLeaseEvent(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
o := oldObj.(*v1.Node)
n := newObj.(*v1.Node)
// 校验节点annotations中flannel.alpha.coreos.com/kube-subnet-manager
if s, ok := n.Annotations[ksm.annotations.SubnetKubeManaged]; !ok || s != "true" {
return
}
// 新旧Node对象的这些annotations是否一样
if o.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendData] == n.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendData] &&
o.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendType] == n.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendType] &&
o.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendPublicIP] == n.Annotations[ksm.annotations.BackendPublicIP] {
return // No change to lease
}
// 解析节点Node annotaions中的子网信息赋值给Lease对象
l, err := ksm.nodeToLease(*n)
if err != nil {
glog.Infof("Error turning node %q to lease: %v", n.ObjectMeta.Name, err)
return
}
// 塞到events channel中
ksm.events <- subnet.Event{subnet.EventAdded, l}
}
在哪里从events channel取呢? 在backend Manager那端获取,backend类型有:alivpc、alloc、awsvpc、extension、gce、hostgw、ipip、ipsec、udp、vxlan
每种backend类型在main启动函数开始时就进行了注册
// Backends need to be imported for their init() to get executed and them to register
"github.com/coreos/flannel/backend"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/alivpc"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/alloc"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/awsvpc"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/extension"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/gce"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/hostgw"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/ipip"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/ipsec"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/udp"
_ "github.com/coreos/flannel/backend/vxlan"
// constructors维护backend类型名称->初始化backend对象函数的map结构
var constructors = make(map[string]BackendCtor)
// 注册函数
func Register(name string, ctor BackendCtor) {
constructors[name] = ctor
}
以hostgw类型为例
// hostgw backend类型注册到constructors
func init() {
backend.Register("host-gw", New)
}
// hostgw backend结构体定义
type HostgwBackend struct {
// 子网管理器
sm subnet.Manager
// 外部网卡属性
extIface *backend.ExternalInterface
}
// 初始化hostgw Backend对象函数
func New(sm subnet.Manager, extIface *backend.ExternalInterface) (backend.Backend, error) {
// 不支持映射IP场景
if !extIface.ExtAddr.Equal(extIface.IfaceAddr) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("your PublicIP differs from interface IP, meaning that probably you're on a NAT, which is not supported by host-gw backend")
}
be := &HostgwBackend{
sm: sm,
extIface: extIface,
}
return be, nil
}
// 每种backend类型都会调用RegisterNetwork这个函数, 每种类型都需要一个新的网络对象,比如操作静态路由、vxlan隧道、udp隧道、ipip隧道等;
// 这些网络对象抽象成一个公共接口Network,返回结果是一个实现了Network接口的对象
type Network interface {
Lease() *subnet.Lease
MTU() int
Run(ctx context.Context)
}
func (be *HostgwBackend) RegisterNetwork(ctx context.Context, wg sync.WaitGroup, config *subnet.Config) (backend.Network, error) {
// 初始化RouteNetwork对象
n := &backend.RouteNetwork{
SimpleNetwork: backend.SimpleNetwork{
ExtIface: be.extIface,
},
SM: be.sm,
BackendType: "host-gw",
Mtu: be.extIface.Iface.MTU,
LinkIndex: be.extIface.Iface.Index,
}
// 获取路由的回调函数,就是到其它节点子网的静态路由
n.GetRoute = func(lease *subnet.Lease) *netlink.Route {
return &netlink.Route{
// 租约节点的网段
Dst: lease.Subnet.ToIPNet(),
// 租约节点的publicIP
Gw: lease.Attrs.PublicIP.ToIP(),
// 本地的link
LinkIndex: n.LinkIndex,
}
}
// 初始化LeaseAttrs对象
attrs := subnet.LeaseAttrs{
PublicIP: ip.FromIP(be.extIface.ExtAddr),
BackendType: "host-gw",
}
// 获取租约节点的子网信息, 这里面主要有三个步骤
// 1. 从nodeStore中根据节点名称获取Node对象, 深拷贝复制个新对象出来
// 2. Patch节点的annotations, 把子网相关信息标注上
// 3. 启动之初,标注网络不可用到Node Condition
l, err := be.sm.AcquireLease(ctx, &attrs)
switch err {
case nil:
// 正常赋值
n.SubnetLease = l
case context.Canceled, context.DeadlineExceeded:
return nil, err
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to acquire lease: %v", err)
}
return n, nil
}
// 继续调用实现了Network接口的对象的Run函数
func (n *RouteNetwork) Run(ctx context.Context) {
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
log.Info("Watching for new subnet leases")
// 初始化一个存放子网event类型的channel
evts := make(chan []subnet.Event)
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
// 监听节点租约变化
subnet.WatchLeases(ctx, n.SM, n.SubnetLease, evts)
wg.Done()
}()
// 路由相关在下面《hostgw模式生成路由》分析
n.routes = make([]netlink.Route, 0, 10)
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
n.routeCheck(ctx)
wg.Done()
}()
defer wg.Wait()
for {
select {
// 从evts channel取event
case evtBatch := <-evts:
// 处理event的函数,涉及路由的添加/删除
n.handleSubnetEvents(evtBatch)
case <-ctx.Done():
return
}
}
}
// subnet.WatchLeases
func WatchLeases(ctx context.Context, sm Manager, ownLease *Lease, receiver chan []Event) {
// 初始化一个leaseWatcher对象
lw := &leaseWatcher{
//ownLease代表本节点的subnet lease
ownLease: ownLease,
}
var cursor interface{}
for {
// 假设subnetManager用的是KubeSubnetManager
// 所以调用的是SubnetManager的WatchLeases, 尝试从events channnel中取出event
res, err := sm.WatchLeases(ctx, cursor)
if err != nil {
if err == context.Canceled || err == context.DeadlineExceeded {
return
}
log.Errorf("Watch subnets: %v", err)
// 获取失败的话,间隔1秒继续尝试
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
// res.Cursor、res.Snapshot都不适用于KubeSubnetManager
cursor = res.Cursor
var batch []Event
// 从evnets channel中取出event
if len(res.Events) > 0 {
// update函数处理两种event,一种是EventAdded,另一种是EventRemoved
// EventAdded:leaseWatcher.leases新增这个event, 如果已存在就替换
// EventRemoved:l = append(l[:i], l[i+1:]...)采用这种方式移除Event
batch = lw.update(res.Events)
} else {
// 如果events channel中没有event的话
// 1. 遍历lw.leases以EventRemoved事件添加到batch中, 把原先的路由都删掉. 其实len(res.Events)压根不会为0,sm.WatchLeases是一个channel select调用,没有事件产生的话,就会阻塞在这里
// 2. 清空lw.leases,以res.Snapshot赋值到lw.leases
batch = lw.reset(res.Snapshot)
}
if len(batch) > 0 {
// 写入receiver channel
receiver <- batch
}
}
}
etcd子网管理器
// 初始化连接etcd的配置信息
cfg := &etcdv2.EtcdConfig{
Endpoints: strings.Split(opts.etcdEndpoints, ","),
Keyfile: opts.etcdKeyfile,
Certfile: opts.etcdCertfile,
CAFile: opts.etcdCAFile,
Prefix: opts.etcdPrefix,
Username: opts.etcdUsername,
Password: opts.etcdPassword,
}
// Attempt to renew the lease for the subnet specified in the subnetFile
// 获取先前的子网配置
prevSubnet := ReadCIDRFromSubnetFile(opts.subnetFile, "FLANNEL_SUBNET")
// 返回一个etcd Manager对象
return etcdv2.NewLocalManager(cfg, prevSubnet)
etcd LocalManager结构体定义
type LocalManager struct {
registry Registry
previousSubnet ip.IP4Net
}
内部还包含一个Registry内部接口定义
type Registry interface {
getNetworkConfig(ctx context.Context) (string, error)
getSubnets(ctx context.Context) ([]Lease, uint64, error)
getSubnet(ctx context.Context, sn ip.IP4Net) (*Lease, uint64, error)
createSubnet(ctx context.Context, sn ip.IP4Net, attrs *LeaseAttrs, ttl time.Duration) (time.Time, error)
updateSubnet(ctx context.Context, sn ip.IP4Net, attrs *LeaseAttrs, ttl time.Duration, asof uint64) (time.Time, error)
deleteSubnet(ctx context.Context, sn ip.IP4Net) error
watchSubnets(ctx context.Context, since uint64) (Event, uint64, error)
watchSubnet(ctx context.Context, since uint64, sn ip.IP4Net) (Event, uint64, error)
}
这些函数定义简化了操作etcd registry子网配置
host-gw模式
New -> RegisterNetwork -> RouteNetwork.Run
更新路由的主要代码
// 初始化routes slice
n.routes = make([]netlink.Route, 0, 10)
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
// 间隔10s检查下子网的路由是否存在,否则加上
n.routeCheck(ctx)
wg.Done()
}()
defer wg.Wait()
for {
select {
case evtBatch := <-evts:
// 处理事件的函数
n.handleSubnetEvents(evtBatch)
case <-ctx.Done():
return
}
}
func (n *RouteNetwork) handleSubnetEvents(batch []subnet.Event) {
// 遍历batch channel
for _, evt := range batch {
switch evt.Type {
// 添加事件
case subnet.EventAdded:
log.Infof("Subnet added: %v via %v", evt.Lease.Subnet, evt.Lease.Attrs.PublicIP)
// Backend类型判断
if evt.Lease.Attrs.BackendType != n.BackendType {
log.Warningf("Ignoring non-%v subnet: type=%v", n.BackendType, evt.Lease.Attrs.BackendType)
continue
}
// 获取到其它节点子网的路由
route := n.GetRoute(&evt.Lease)
// 因为是添加事件,添加n.routes中的路由
n.addToRouteList(*route)
// Check if route exists before attempting to add it
// 再次检查路由是否已存在
routeList, err := netlink.RouteListFiltered(netlink.FAMILY_V4, &netlink.Route{Dst: route.Dst}, netlink.RT_FILTER_DST)
if err != nil {
log.Warningf("Unable to list routes: %v", err)
}
if len(routeList) > 0 && !routeEqual(routeList[0], *route) {
// Same Dst different Gw or different link index. Remove it, correct route will be added below.
log.Warningf("Replacing existing route to %v via %v dev index %d with %v via %v dev index %d.", evt.Lease.Subnet, routeList[0].Gw, routeList[0].LinkIndex, evt.Lease.Subnet, evt.Lease.Attrs.PublicIP, route.LinkIndex)
if err := netlink.RouteDel(&routeList[0]); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Error deleting route to %v: %v", evt.Lease.Subnet, err)
continue
}
n.removeFromRouteList(routeList[0])
}
if len(routeList) > 0 && routeEqual(routeList[0], *route) {
// Same Dst and same Gw, keep it and do not attempt to add it.
log.Infof("Route to %v via %v dev index %d already exists, skipping.", evt.Lease.Subnet, evt.Lease.Attrs.PublicIP, routeList[0].LinkIndex)
} else if err := netlink.RouteAdd(route); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Error adding route to %v via %v dev index %d: %v", evt.Lease.Subnet, evt.Lease.Attrs.PublicIP, route.LinkIndex, err)
continue
}
// 删除事件
case subnet.EventRemoved:
log.Info("Subnet removed: ", evt.Lease.Subnet)
// Backend类型不匹配的话,跳过
if evt.Lease.Attrs.BackendType != n.BackendType {
log.Warningf("Ignoring non-%v subnet: type=%v", n.BackendType, evt.Lease.Attrs.BackendType)
continue
}
// 获取到其它节点子网的路由
route := n.GetRoute(&evt.Lease)
// Always remove the route from the route list.
// 因为是删除事件,删除n.routes中的路由
n.removeFromRouteList(*route)
// 因为是删除事件,所以删除宿主机上的路由
if err := netlink.RouteDel(route); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Error deleting route to %v: %v", evt.Lease.Subnet, err)
continue
}
default:
log.Error("Internal error: unknown event type: ", int(evt.Type))
}
}
}
galaxy+flannel+host-gw手动实践
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
ip netns add test1
ip link add veth1 type veth peer name eth0 netns test1
ip link set up dev veth1
ip addr add 1.1.1.1/32 dev veth1
ip netns exec test1 ip link set eth0 up
ip netns exec test1 ip link set lo up
ip netns exec test1 ip addr add 1.1.1.2/32 dev eth0
ip route add 1.1.1.2/32 dev veth1 scope link
# 容器内部添加路由
ip netns exec test1 ip route add 169.254.1.1 dev eth0 scope link
ip netns exec test1 ip route add default via 169.254.1.1 dev eth0
ip netns exec test1 ip neigh replace 169.254.1.1 dev eth0 lladdr <宿主机veth1的MAC地址>
在宿主机上进行对1.1.1.2的ping连通测试,连通可达.
vxlan模式
vxlan介绍
Linux 对 VXLAN 协议的支持时间并不久,2012年Stephen Hemminger才把相关的工作合并到kernel中,并最终出现在kernel 3.7.0版本。 为了稳定性和很多的功能,可能会看到某些软件推荐在3.9.0或者3.10.0以后版本的kernel上使用VXLAN。 到了 kernel 3.12版本,Linux对VXLAN的支持已经完备,支持单播和组播,IPv4和IPv6。利用man查看ip的link子命令,可以查看是否有VXLAN type:
#查看vxlan是否支持ipv6
# lsmod |grep vxlan
vxlan 69632 0
ip6_udp_tunnel 16384 1 vxlan
udp_tunnel 16384 1 vxlan
VXLAN的全称为Virtual eXtensible LAN,从名称看,它的目标就是扩展VLAN协议。802.1Q的VLAN TAG只占12位,只能提供4096个网络标识符。 而在VXLAN中,标识符扩展到24位,能提供16777216个逻辑网络标识符,VXLAN的标识符称为VNI(VXLAN Network Identifier)。 另外,VLAN只能应用在一个二层网络中,而VXLAN通过将原始二层以太网帧封装在IP协议包中,在IP基础网络之上构建overlay的逻辑大二层网络。
vxlan将二层数据帧封装在UDP数据包中,包结构如下:
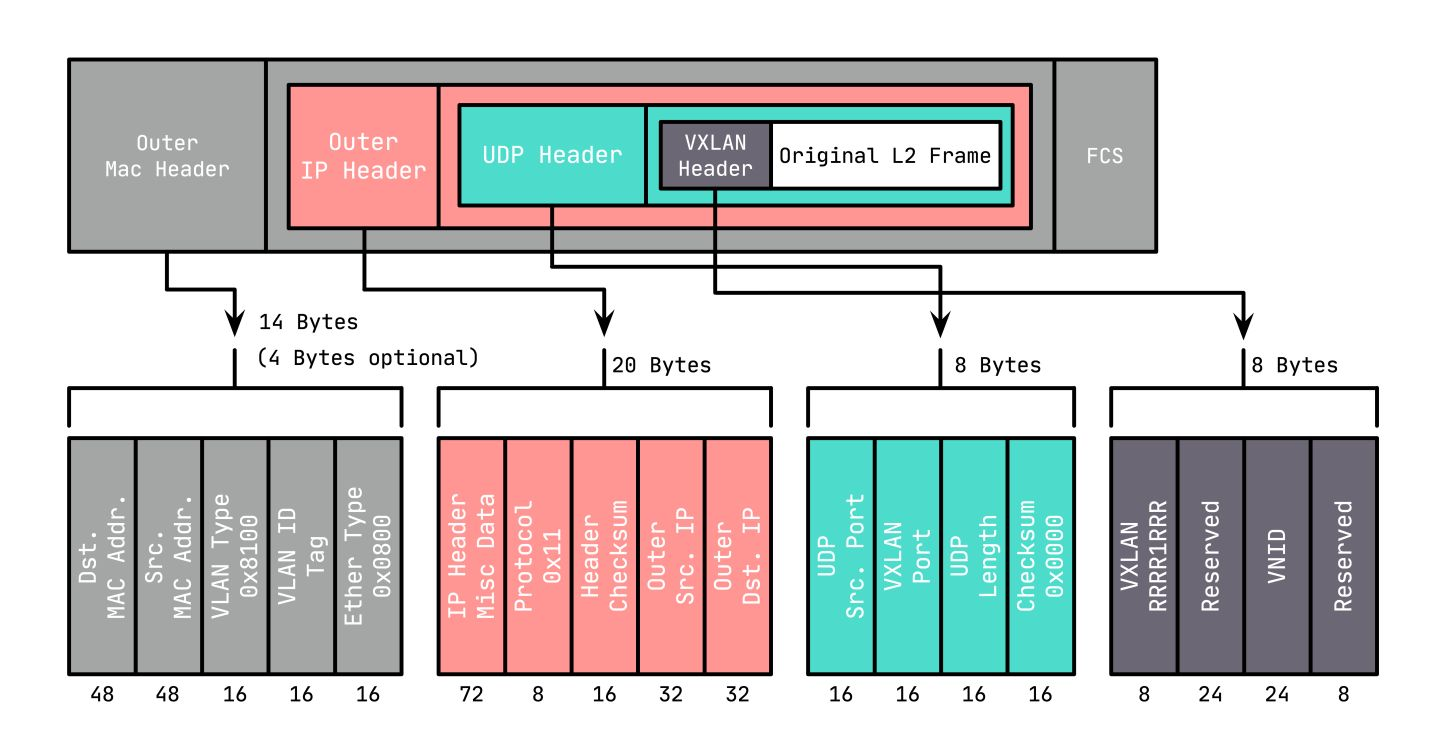
从包结构上可以看到,VXLAN会额外消耗50字节的空间。 为了防止因数据包大小超过网络设备的MTU值而被丢弃,需要将VM的MTU减少50甚至更多,或者调整中间网络设备的MTU。 VXLAN协议中将对原始数据包进行封装和解封装的设备称为VTEP(VXLAN Tunnel End Point),它可以由硬件设备实现,也可以由软件实现。
我们来看VXLAN的通信过程。在上图的虚拟机VM1和VM2处于逻辑二层网络中。VM1发出的二层以太网帧由VTEP封装进IP数据包,之后发送到VM2所在主机。 VM2所在主机接收到IP报文后,解封装出原始的以太网帧再转发给VM2。然而,VM1所在主机的VTEP做完数据封装后,如何知道要将封装后的数据包发到哪个VTEP呢? 实际上,VTEP通过查询转发表来确定目标VTEP地址,而转发表通过泛洪和学习机制来构建。目标MAC地址在转发表中不存在的流量称为未知单播(Unknown unicast)。 广播(broadcast)、未知单播(unknown unicast)和组播(multicast)一般统称为BUM流量。 VXLAN规范要求BUM流量使用IP组播进行洪泛,将数据包发送到除源VTEP外的所有VTEP。 目标VTEP发送回响应数据包时,源VTEP从中学习MAC地址、VNI和VTEP的映射关系,并添加到转发表中。 后续VTEP再次发送数据包给该MAC地址时,VTEP会从转发表中直接确定目标VTEP,从而只发送单播数据到目标VTEP。
OpenvSwitch没有实现IP组播,而是使用多个单播来实现洪泛。洪泛流量本身对性能有一定影响,可以通过由controller收集相应信息来填充转发表而避免洪泛。
Linux环境中常用的VXLAN实现有两种:
- Linux内核实现
- OpenvSwitch实现
对于大规模的VXLAN网络中,最核心的问题一般有两个:
- 如何发现网络中其他VTEP
- 如何降低BUM(Broadcast, Unknown unicast, Multicast)流量
在对于问题一来说,解决方法是洪泛,对于问题二,则通过源地址学习来确定MAC地址的归属。 VXLAN的转发过程主要依赖FDB(Forwarding Database)实现。二层网桥的FDB表项格式可表达为:
<MAC> <VLAN> <DEV PORT>
VXLAN设备的表项与之类似,可以表达为:
<MAC> <VNI> <REMOTE IP>
VXLAN设备根据MAC地址来查找相应的VTEP IP地址,继而将二层数据帧封装发送至相应VTEP。 如果我们能够从集中的Controller或者存储中获取VTEP信息以及MAC地址与VTEP的对应信息, 则问题一和问题二都可以通过根据相应信息动态更新FDB表项来解决,OpenStack的Neutron, VMware的NSX,Docker Overlay都有类似的思路。
手动实践
手动更新FDB表来实现VXLAN通信,实验环境,如下图
node1 192.168.104.111
node2 192.168.104.128
+-------------------------+ +-------------------------+
| | | |
| +------------+ | | +------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | 3.3.3.4 | | | | 3.3.3.3 | |
| +------------+ | | +------------+ |
| |eth0 | | |eth0 |
| | | | | |
| +veth0 | | +veth0 |
| +------------+ | | +------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | br1 | | | | br1 | |
| +-----+------+ | | +-----+------+ |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| +-----+------+ | | +-----+------+ |
| | vxlan100 | | | | vxlan100 | |
| | | | | | | |
| +-----+------+ | | +-----+------+ |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
node2 | | eth0 | | | eth0 | node1
+-------------------------+ +-------------------------+
| 192.168.104.128 192.168.104.111|
| |
| |
+-----------+-----------------------------------------+---------------+
node1操作
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
ip netns add test1
ip link add veth1 type veth peer name eth0 netns test1
ip netns exec test1 ip link set eth0 up
ip netns exec test1 ip link set lo up
ip netns exec test1 ip addr add 3.3.3.3/24 dev eth0
ip link set up dev veth1
ip link add br1 type bridge
ip link set br1 up
ip link set veth1 master br1
#指定了nolearning来禁用源地址学习, 通过ip -d a可以看到设备属性
ip link add vxlan100 type vxlan id 100 dstport 4789 local 192.168.104.111 nolearning
ip link set vxlan100 master br1
ip link set up vxlan100
node2操作
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
ip netns add test1
ip link add veth1 type veth peer name eth0 netns test1
ip netns exec test1 ip link set eth0 up
ip netns exec test1 ip link set lo up
ip netns exec test1 ip addr add 3.3.3.4/24 dev eth0
ip link set up dev veth1
ip link add br1 type bridge
ip link set br1 up
ip link set veth1 master br1
ip link add vxlan100 type vxlan id 100 dstport 4789 local 192.168.104.128 nolearning
ip link set vxlan100 master br1
ip link set up vxlan100
node1上的test1访问不了node2的3.3.3.4
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c 2 3.3.3.4
PING 3.3.3.4 (3.3.3.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 3.3.3.3 icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
From 3.3.3.3 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable
--- 3.3.3.4 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 0 received, +2 errors, 100% packet loss, time 1000ms
pipe 2
node1上的3.3.3.3接口需要先发送arp广播查询3.3.3.4的mac地址。arp广播到达设备vxlan100后,根据FDB表没有找到VTEP地址
分别查看node1、node2 test1命名空间里的接口mac地址
#node1 test1命名空间里的接口mac地址
# ip netns exec test1 ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0@if42: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether ea:da:ea:f7:13:be brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 3.3.3.3/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::e8da:eaff:fef7:13be/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#node2 test1命名空间里的接口mac地址
# ip netns exec test1 ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0@if15: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 3.3.3.4/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::84a7:37ff:fee5:4fe0/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
node1上增加vxlan FDB表项
# bridge fdb append 00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.128
#添加的是对端的mac地址和ip
# bridge fdb append 86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.128
# bridge fdb show brport vxlan100
66:42:78:42:a4:76 vlan 1 master br1 permanent
66:42:78:42:a4:76 master br1 permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dst 192.168.104.128 self permanent
86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 dst 192.168.104.128 self permanent
全零表项表示没有匹配的MAC地址时,就发送到该表项中的VTEP, 用于处理BUM流量. 查看VXLAN设备vxlan100的FDB表项,两条表项都已成功添加而且永不老化(permanent)
node2上增加vxlan FDB表项
# bridge fdb append 00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.111
# bridge fdb append ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.111
# bridge fdb show brport vxlan100
36:b2:8d:92:e8:97 vlan 1 master br1 permanent
36:b2:8d:92:e8:97 master br1 permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dst 192.168.104.111 self permanent
ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dst 192.168.104.111 self permanent
再次ping测试,可以互相连通了
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.4
PING 3.3.3.4 (3.3.3.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 3.3.3.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=2.21 ms
64 bytes from 3.3.3.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.631 ms
--- 3.3.3.4 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.631/1.423/2.215/0.792 ms
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.3
PING 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 3.3.3.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.687 ms
64 bytes from 3.3.3.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.982 ms
--- 3.3.3.3 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.687/0.834/0.982/0.150 ms
node1节点上的test1命名空间里的eth0(3.3.3.3)访问node2节点上的test1命名空间里的eth0(3.3.3.4)时,需要发送arp广播先获得3.3.3.4的mac地址。
在大规模vxlan环境中,arp广播非常消耗资源;其实如果能在本地获取到mac所在的VTEP,可以由vxlan设备实现arp代答,linux vxlan设备支持通过设置proxy参数开启arp代答,将arp广播范围控制在本地。
node1上重新创建VXLAN接口、开启ARP代答并重新添加FDB表项
ip link del vxlan100
ip link add vxlan100 type vxlan id 100 dstport 4789 local 192.168.104.111 nolearning proxy
ip link set vxlan100 master br1
ip link set up vxlan100
bridge fdb append 00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.128
bridge fdb append 86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.128
# 添加vxlan设备arp代答
ip neighbor add 3.3.3.4 lladdr 86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 dev vxlan100
# ip neighbor show dev vxlan100
3.3.3.4 lladdr 86:a7:37:e5:4f:e0 PERMANENT
可以通过ip neighbor(可以简写为ip neigh)命令管理ARP缓存
node2上同样的操作, 重新创建VXLAN接口、开启ARP代答并重新添加FDB表项
ip link del vxlan100
ip link add vxlan100 type vxlan id 100 dstport 4789 local 192.168.104.128 nolearning proxy
ip link set vxlan100 master br1
ip link set up vxlan100
bridge fdb append 00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.111
bridge fdb append ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.111
# 添加vxlan设备arp代答
ip neighbor add 3.3.3.3 lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dev vxlan100
# ip neighbor show dev vxlan100
3.3.3.3 lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be PERMANENT
再次测试连通性
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.4
PING 3.3.3.4 (3.3.3.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 3.3.3.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.16 ms
64 bytes from 3.3.3.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.619 ms
--- 3.3.3.4 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.619/0.891/1.164/0.274 ms
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.3
PING 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 3.3.3.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.75 ms
64 bytes from 3.3.3.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.855 ms
--- 3.3.3.3 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.855/1.303/1.751/0.448 ms
为了支持更加灵活的维护ARP和FDB表,Linux的VXLAN设备还支持对于表项匹配MISS的消息通知。内核在发现在ARP或者FDB表项中找不到相应的表项, 则可以通过NETLINK消息发送通知,用户态进程可以监听相应消息并补充所缺失的表项记录,从而实现动态的表项维护。
VXLAN设备支持两种消息:
- L2MISS: VXLAN设备在FDB表中找不到目的MAC地址所属的VTEP IP地址。L2MISS消息的发送需要满足如下条件:
- 目的MAC地址未知,即在FDB表中没有相应条项
- FDB表中没有全零表项
- 目的MAC地址不是组播或多播地址
- L3MISS: VXLAN设备在ARP表中找不到目的IP所对应的MAC地址
node2上删除vxlan100,重新添加开启l2miss和l3miss的vxlan100接口
ip link del vxlan100
ip link add vxlan100 type vxlan id 100 dstport 4789 local 192.168.104.128 nolearning proxy l2miss l3miss
ip link set vxlan100 master br1
ip link set up vxlan100
#开另一个shell执行
# ip monitor all dev vxlan100
清除test1命名空间里的arp缓存, 然后ping测试
ip netns exec test1 ip neigh flush all
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.3
PING 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 3.3.3.4 icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
From 3.3.3.4 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable
--- 3.3.3.3 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 0 received, +2 errors, 100% packet loss, time 999ms
pipe 2
ip monitor收到L3MISS的消息
[NEIGH]miss 3.3.3.3 STALE
[NEIGH]miss 3.3.3.3 STALE
手动添加arp缓存
ip neighbor replace 3.3.3.3 lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dev vxlan100 nud reachable
# ip neighbor show dev vxlan100
3.3.3.3 lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be REACHABLE
nud reachable, NUD表示: Neighbour Unreachability Detection, 代表这个表项有过期时间,系统发现它无效后过一定时间会自动删除,
之后如果再次需要内核会再次发送L3MISS消息,这样就不用自己维护这些添加的表项了
再次进行ping测试,ip monitor收到L2MISS消息
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.3.3
PING 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 3.3.3.4 icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
From 3.3.3.4 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable
--- 3.3.3.3 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 0 received, +2 errors, 100% packet loss, time 999ms
pipe 2
[NEIGH]miss lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be STALE
[NEIGH]miss lladdr ea:da:ea:f7:13:be STALE
node2上继续添加FDB表项
bridge fdb append ea:da:ea:f7:13:be dev vxlan100 dst 192.168.104.111
再次ping测试,可以连通了
flannel vxlan手动实践
Docker的libnetwork VXLAN模式以及Flannel的VXLAN模式都使用类似上述模式来实现Docker overlay网络,具体操作如下
通过man ip-link和man ip-netns可以查看命令使用方式,还可以man其它子命令
ip-address(8), ip-addrlabel(8), ip-l2tp(8), ip-link(8), ip-maddress(8), ip-monitor(8), ip-mroute(8), ip-neighbour(8), ip-netns(8),
ip-ntable(8), ip-route(8), ip-rule(8), ip-tcp_metrics(8), ip-token(8), ip-tunnel(8), ip-xfrm(8)
node1操作
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
ip netns add test1
ip link add veth1 type veth peer name eth0 netns test1
ip netns exec test1 ip link set eth0 up
ip netns exec test1 ip link set lo up
ip netns exec test1 ip addr add 3.3.1.3/24 dev eth0
ip netns exec test1 ifconfig eth0 mtu 1450
ip link set up dev veth1
ip link add cni0 type bridge
ip link set cni0 up
ip link set veth1 master cni0
ip link add flannel.1 type vxlan id 1 dstport 8472 local 192.168.104.111 nolearning proxy
ip addr add 3.3.1.1/24 dev cni0
ip addr add 3.3.1.0/32 dev flannel.1
ip netns exec test1 ip route add 0.0.0.0/0 via 3.3.1.1
ifconfig veth1 mtu 1450
ifconfig flannel.1 mtu 1450
node2操作
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
ip netns add test1
ip link add veth1 type veth peer name eth0 netns test1
ip netns exec test1 ip link set eth0 up
ip netns exec test1 ip link set lo up
ip netns exec test1 ip addr add 3.3.2.4/24 dev eth0
ip netns exec test1 ifconfig eth0 mtu 1450
ip link set up dev veth1
ip link add cni0 type bridge
ip link set cni0 up
ip link set veth1 master cni0
ip link add flannel.1 type vxlan id 1 dstport 8472 local 192.168.104.128 nolearning proxy
ip addr add 3.3.2.1/24 dev cni0
ip addr add 3.3.2.0/32 dev flannel.1
ip netns exec test1 ip route add 0.0.0.0/0 via 3.3.2.1
ifconfig veth1 mtu 1450
ifconfig flannel.1 mtu 1450
node1路由/fdb/arp缓存设置
ip route add 3.3.2.0/24 via 3.3.2.0 dev flannel.1 onlink
bridge fdb append ca:d2:6d:70:20:fd dev flannel.1 dst 192.168.104.128
ip neighbor add 3.3.2.0 lladdr ca:d2:6d:70:20:fd dev flannel.1
node2路由/fdb/arp缓存设置
ip route add 3.3.1.0/24 via 3.3.1.0 dev flannel.1 onlink
bridge fdb append 42:10:c8:96:4e:e4 dev flannel.1 dst 192.168.104.111
ip neighbor add 3.3.1.0 lladdr 42:10:c8:96:4e:e4 dev flannel.1
通过增加ip route add 3.3.2.0/24 via 3.3.2.0 dev flannel.1 onlink和ip route add 3.3.1.0/24 via 3.3.1.0 dev flannel.1 onlink路由,
使得访问3.3.2.0/24网段的目的IP都通过flannel.1出去,回包的路由也有。
3.3.1.3到3.3.2.4的连通性,测试可达
# ip netns exec test1 ping -c2 3.3.2.4
PING 3.3.2.4 (3.3.2.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 3.3.2.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=1.12 ms
64 bytes from 3.3.2.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=62 time=0.601 ms
--- 3.3.2.4 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.601/0.863/1.125/0.262 ms
代码分析
调用流程
New -> RegisterNetwork -> network.Run(flannel/backend/vxlan/vxlan_network.go)
每种backend类型都会调用RegisterNetwork这个函数, 每种类型都需要一个新的网络对象,比如操作静态路由、vxlan隧道、udp隧道、ipip隧道等; 这些网络对象抽象成一个公共接口Network,返回结果是一个实现了Network接口的对象
type network struct {
backend.SimpleNetwork
dev *vxlanDevice
subnetMgr subnet.Manager
}
func (be *VXLANBackend) RegisterNetwork(ctx context.Context, wg *sync.WaitGroup, config *subnet.Config) (backend.Network, error) {
// Parse our configuration
cfg := struct {
// vxlan id, 默认1
VNI int
// vxlan的目的UDP端口号, 默认是0,自动分配出来的端口号是8472
Port int
// 启用VXLAN Group Based Policy
GBP bool
// 启用源地址学习, 也就是VXLAN的flood and learn,甚少被使用
Learning bool
// 当主机位于同一子网中时,启用直接路由(类似host-gw);VXLAN仅用于将数据包封装到不同子网中的主机。
DirectRouting bool
}{
VNI: defaultVNI,
}
if len(config.Backend) > 0 {
// 解析Backend参数
if err := json.Unmarshal(config.Backend, &cfg); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error decoding VXLAN backend config: %v", err)
}
}
log.Infof("VXLAN config: VNI=%d Port=%d GBP=%v Learning=%v DirectRouting=%v", cfg.VNI, cfg.Port, cfg.GBP, cfg.Learning, cfg.DirectRouting)
devAttrs := vxlanDeviceAttrs{
vni: uint32(cfg.VNI),
name: fmt.Sprintf("flannel.%v", cfg.VNI),
vtepIndex: be.extIface.Iface.Index,
vtepAddr: be.extIface.IfaceAddr,
vtepPort: cfg.Port,
gbp: cfg.GBP,
learning: cfg.Learning,
}
// 创建vxlan接口设备
dev, err := newVXLANDevice(&devAttrs)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
dev.directRouting = cfg.DirectRouting
// 初始化LeaseAttrs对象
subnetAttrs, err := newSubnetAttrs(be.extIface.ExtAddr, dev.MACAddr())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 获取租约节点的子网信息
lease, err := be.subnetMgr.AcquireLease(ctx, subnetAttrs)
switch err {
case nil:
case context.Canceled, context.DeadlineExceeded:
return nil, err
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to acquire lease: %v", err)
}
// Ensure that the device has a /32 address so that no broadcast routes are created.
// This IP is just used as a source address for host to workload traffic (so
// the return path for the traffic has an address on the flannel network to use as the destination)
if err := dev.Configure(ip.IP4Net{IP: lease.Subnet.IP, PrefixLen: 32}); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to configure interface %s: %s", dev.link.Attrs().Name, err)
}
// 返回结果是一个实现了Network接口的对象
return newNetwork(be.subnetMgr, be.extIface, dev, ip.IP4Net{}, lease)
}
func newVXLANDevice(devAttrs *vxlanDeviceAttrs) (*vxlanDevice, error) {
link := &netlink.Vxlan{
LinkAttrs: netlink.LinkAttrs{
Name: devAttrs.name,
},
VxlanId: int(devAttrs.vni),
VtepDevIndex: devAttrs.vtepIndex,
SrcAddr: devAttrs.vtepAddr,
Port: devAttrs.vtepPort,
Learning: devAttrs.learning,
GBP: devAttrs.gbp,
}
link, err := ensureLink(link)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 禁用vxlan网卡ipv6的自动配置
_, _ = sysctl.Sysctl(fmt.Sprintf("net/ipv6/conf/%s/accept_ra", devAttrs.name), "0")
return &vxlanDevice{
link: link,
}, nil
}
最终会调用到network对象的Run函数
func (nw *network) Run(ctx context.Context) {
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
log.V(0).Info("watching for new subnet leases")
events := make(chan []subnet.Event)
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
subnet.WatchLeases(ctx, nw.subnetMgr, nw.SubnetLease, events)
log.V(1).Info("WatchLeases exited")
wg.Done()
}()
defer wg.Wait()
for {
select {
case evtBatch := <-events:
// 处理事件的函数
nw.handleSubnetEvents(evtBatch)
case <-ctx.Done():
return
}
}
}
func (nw *network) handleSubnetEvents(batch []subnet.Event) {
// 遍历batch channel
for _, event := range batch {
// 获取子网信息
sn := event.Lease.Subnet
attrs := event.Lease.Attrs
if attrs.BackendType != "vxlan" {
log.Warningf("ignoring non-vxlan subnet(%s): type=%v", sn, attrs.BackendType)
continue
}
var vxlanAttrs vxlanLeaseAttrs
// 解析BackendData,形如flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-data: '{"VtepMAC":"96:11:83:87:ea:56"}'
if err := json.Unmarshal(attrs.BackendData, &vxlanAttrs); err != nil {
log.Error("error decoding subnet lease JSON: ", err)
continue
}
// 到对端vxlan隧道的路由,形如172.20.1.0/24 via 172.20.1.0 dev flannel.1 onlink
// This route is used when traffic should be vxlan encapsulated
vxlanRoute := netlink.Route{
LinkIndex: nw.dev.link.Attrs().Index,
Scope: netlink.SCOPE_UNIVERSE,
Dst: sn.ToIPNet(),
Gw: sn.IP.ToIP(),
}
// 路由onlink参数: 假装和下一跳路由器是直接相连的,即使它没有匹配任何接口前缀 (prefix)
vxlanRoute.SetFlag(syscall.RTNH_F_ONLINK)
// 直连的路由,下一跳是其它节点的外网网卡地址,形如172.20.1.0/24 via 192.168.104.128 dev eth0
// directRouting is where the remote host is on the same subnet so vxlan isn't required.
directRoute := netlink.Route{
Dst: sn.ToIPNet(),
Gw: attrs.PublicIP.ToIP(),
}
var directRoutingOK = false
// 启用直连路由模式
if nw.dev.directRouting {
// 判断下一跳地址是否处于同一子网
if dr, err := ip.DirectRouting(attrs.PublicIP.ToIP()); err != nil {
log.Error(err)
} else {
directRoutingOK = dr
}
}
switch event.Type {
case subnet.EventAdded:
// 启用直连路由模式
if directRoutingOK {
log.V(2).Infof("Adding direct route to subnet: %s PublicIP: %s", sn, attrs.PublicIP)
// 创建直连路由
if err := netlink.RouteReplace(&directRoute); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Error adding route to %v via %v: %v", sn, attrs.PublicIP, err)
continue
}
// 非直连路由模式下
} else {
log.V(2).Infof("adding subnet: %s PublicIP: %s VtepMAC: %s", sn, attrs.PublicIP, net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC))
// 添加vxlan设备arp代答,前面也没有设置vxlan接口proxy属性?
if err := nw.dev.AddARP(neighbor{IP: sn.IP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("AddARP failed: ", err)
continue
}
// 添加对端VTEP FDB表项
if err := nw.dev.AddFDB(neighbor{IP: attrs.PublicIP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("AddFDB failed: ", err)
// Try to clean up the ARP entry then continue
if err := nw.dev.DelARP(neighbor{IP: event.Lease.Subnet.IP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("DelARP failed: ", err)
}
continue
}
// Set the route - the kernel would ARP for the Gw IP address if it hadn't already been set above so make sure
// this is done last.
// 创建vxlan路由
if err := netlink.RouteReplace(&vxlanRoute); err != nil {
log.Errorf("failed to add vxlanRoute (%s -> %s): %v", vxlanRoute.Dst, vxlanRoute.Gw, err)
// 删除arp缓存
// Try to clean up both the ARP and FDB entries then continue
if err := nw.dev.DelARP(neighbor{IP: event.Lease.Subnet.IP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("DelARP failed: ", err)
}
// 删除FDB表项
if err := nw.dev.DelFDB(neighbor{IP: event.Lease.Attrs.PublicIP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("DelFDB failed: ", err)
}
continue
}
}
case subnet.EventRemoved:
if directRoutingOK {
log.V(2).Infof("Removing direct route to subnet: %s PublicIP: %s", sn, attrs.PublicIP)
// 删除直连路由
if err := netlink.RouteDel(&directRoute); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Error deleting route to %v via %v: %v", sn, attrs.PublicIP, err)
}
} else {
log.V(2).Infof("removing subnet: %s PublicIP: %s VtepMAC: %s", sn, attrs.PublicIP, net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC))
// 删除arp缓存
// Try to remove all entries - don't bail out if one of them fails.
if err := nw.dev.DelARP(neighbor{IP: sn.IP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("DelARP failed: ", err)
}
// 删除FDB
if err := nw.dev.DelFDB(neighbor{IP: attrs.PublicIP, MAC: net.HardwareAddr(vxlanAttrs.VtepMAC)}); err != nil {
log.Error("DelFDB failed: ", err)
}
// 删除vxlan路由
if err := netlink.RouteDel(&vxlanRoute); err != nil {
log.Errorf("failed to delete vxlanRoute (%s -> %s): %v", vxlanRoute.Dst, vxlanRoute.Gw, err)
}
}
default:
log.Error("internal error: unknown event type: ", int(event.Type))
}
}
}
建立vxlan通信的过程基本跟手动实践vxlan通信一致,只不过代码中没有看到设置vxlan接口proxy的属性.
基于flannel的固定ip/mac实现
结合flannel cni二进制源码和cni配置文件中可以得出,默认情况下flannel用的ipam是host-local,创建设备插件用的是bridge.
cni-conf.json: |
{
"name": "cbr0",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "flannel",
"fixedIP": true,
"delegate": {
"hairpinMode": true,
"isDefaultGateway": true
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {
"portMappings": true
}
}
]
}
思考1:基于flannel实现原地pod固定ip,改造host-local插件就可以?
是的,host-local是基于本地的ip分配机制,按ip递增的方式来分配,每次分配新的ip都会更新记录
/var/lib/cni/networks/cbr0/last_reserved_ip.0文件中(文件锁保证多写),在这个基础上新增逻辑:如果启动固定ip/mac开关,也一并记录<pod命名空间>-<pod名称>和ip的映射关系,每次本地重启的时候先从本地映射 关系中获取,如果没有获取到,还是走原来的逻辑.
思考2:基于flannel实现原地pod固定mac,改造bridge插件就可以?
是的,如果启动固定ip/mac开关,记录<pod命名空间>-<pod名称>和mac的映射关系,每次本地重启的时候先从本地映射 关系中获取,如果没有获取到,还是走原来的逻辑.
如果是基于crd的方式,可以做到全局pod固定ip/mac,不管是否发生pod迁移,不过需要能访问到k8s apiserver,不太符合 边缘计算场景下的离线情况。
代码片段
网络开发可重复利用的代码片段
package ip
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"net"
"syscall"
"github.com/vishvananda/netlink"
)
// 获取网卡IP
func getIfaceAddrs(iface *net.Interface) ([]netlink.Addr, error) {
link := &netlink.Device{
netlink.LinkAttrs{
Index: iface.Index,
},
}
return netlink.AddrList(link, syscall.AF_INET)
}
// 获取网卡ipv4 IP
func GetIfaceIP4Addr(iface *net.Interface) (net.IP, error) {
addrs, err := getIfaceAddrs(iface)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// prefer non link-local addr
var ll net.IP
for _, addr := range addrs {
if addr.IP.To4() == nil {
continue
}
if addr.IP.IsGlobalUnicast() {
return addr.IP, nil
}
if addr.IP.IsLinkLocalUnicast() {
ll = addr.IP
}
}
if ll != nil {
// didn't find global but found link-local. it'll do.
return ll, nil
}
return nil, errors.New("No IPv4 address found for given interface")
}
// 网卡IP匹配
func GetIfaceIP4AddrMatch(iface *net.Interface, matchAddr net.IP) error {
addrs, err := getIfaceAddrs(iface)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for _, addr := range addrs {
// Attempt to parse the address in CIDR notation
// and assert it is IPv4
if addr.IP.To4() != nil {
if addr.IP.To4().Equal(matchAddr) {
return nil
}
}
}
return errors.New("No IPv4 address found for given interface")
}
// 获取默认网关所在的网卡
func GetDefaultGatewayIface() (*net.Interface, error) {
routes, err := netlink.RouteList(nil, syscall.AF_INET)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
for _, route := range routes {
if route.Dst == nil || route.Dst.String() == "0.0.0.0/0" {
if route.LinkIndex <= 0 {
return nil, errors.New("Found default route but could not determine interface")
}
return net.InterfaceByIndex(route.LinkIndex)
}
}
return nil, errors.New("Unable to find default route")
}
// 根据IP获取网卡
func GetInterfaceByIP(ip net.IP) (*net.Interface, error) {
ifaces, err := net.Interfaces()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
for _, iface := range ifaces {
err := GetIfaceIP4AddrMatch(&iface, ip)
if err == nil {
return &iface, nil
}
}
return nil, errors.New("No interface with given IP found")
}
// 根据IP获取直连路由
func DirectRouting(ip net.IP) (bool, error) {
routes, err := netlink.RouteGet(ip)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("couldn't lookup route to %v: %v", ip, err)
}
if len(routes) == 1 && routes[0].Gw == nil {
// There is only a single route and there's no gateway (i.e. it's directly connected)
return true, nil
}
return false, nil
}
// 确保Link设备是ipv4地址
// EnsureV4AddressOnLink ensures that there is only one v4 Addr on `link` and it equals `ipn`.
// If there exist multiple addresses on link, it returns an error message to tell callers to remove additional address.
func EnsureV4AddressOnLink(ipn IP4Net, link netlink.Link) error {
addr := netlink.Addr{IPNet: ipn.ToIPNet()}
existingAddrs, err := netlink.AddrList(link, netlink.FAMILY_V4)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// flannel will never make this happen. This situation can only be caused by a user, so get them to sort it out.
if len(existingAddrs) > 1 {
return fmt.Errorf("link has incompatible addresses. Remove additional addresses and try again. %#v", link)
}
// If the device has an incompatible address then delete it. This can happen if the lease changes for example.
if len(existingAddrs) == 1 && !existingAddrs[0].Equal(addr) {
if err := netlink.AddrDel(link, &existingAddrs[0]); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to remove IP address %s from %s: %s", ipn.String(), link.Attrs().Name, err)
}
existingAddrs = []netlink.Addr{}
}
// Actually add the desired address to the interface if needed.
if len(existingAddrs) == 0 {
if err := netlink.AddrAdd(link, &addr); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to add IP address %s to %s: %s", ipn.String(), link.Attrs().Name, err)
}
}
return nil
}
参考链接
「真诚赞赏,手留余香」
真诚赞赏,手留余香
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付
